The psychology of consumer behavior is a fascinating field that delves into the complex interplay of psychological, emotional, social, and environmental factors influencing purchasing decisions. From everyday choices to major buying decisions, understanding why we buy what we buy is essential for businesses looking to connect with their target audience. By tapping into these underlying factors, companies can craft marketing strategies that not only resonate deeply with consumers but also foster long-term brand loyalty. This article uncovers the internal and external influences shaping consumer decisions and offers insights into how marketing can align with these behaviors to drive success.
Unlock the Secrets Behind Consumer Behavior!
Curious about what drives our purchasing decisions? Download the full research paper, The Psychology of Consumer Behavior: Why We Buy What We Buy, and gain valuable insights into the emotional, psychological, and social factors that influence why we buy what we buy. Perfect for marketers, business owners, and anyone fascinated by consumer psychology.
Foundations of Consumer Behavior
Definition and Scope of Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior encompasses the actions consumers take when selecting, purchasing, using, and disposing of products and services. This multi-stage process is influenced by a variety of psychological, personal, social, and economic factors. For marketers, understanding consumer behavior is essential to creating strategies that address consumers at each step of their buying journey—from pre-purchase research to post-purchase reflection.
In today’s marketplace, consumer behavior is more than just a simple transaction; it’s a reflection of personal values, social influence, and environmental factors. By understanding this, brands can better connect with their customers, fostering long-term loyalty.
The Three Stages of Buying: Pre-Purchase, Purchase, and Post-Purchase
- Pre-Purchase: This stage involves need recognition and information search. Consumers identify a need or desire, which can be triggered by internal factors (such as hunger) or external stimuli (such as an advertisement). During this stage, they evaluate different options, searching for the best product that meets their needs.
- Purchase: This is the action stage where the consumer makes a decision to buy a product. Factors such as price, convenience, and emotional triggers often influence this step. Impulse buying, often driven by marketing or promotions, plays a big role here.
- Post-Purchase: After the purchase, consumers evaluate their experience with the product or service. If satisfied, they may become loyal customers and recommend the product. Dissatisfaction can lead to returns or negative reviews, which impact future sales.
The Psychology of Consumer Behavior Process
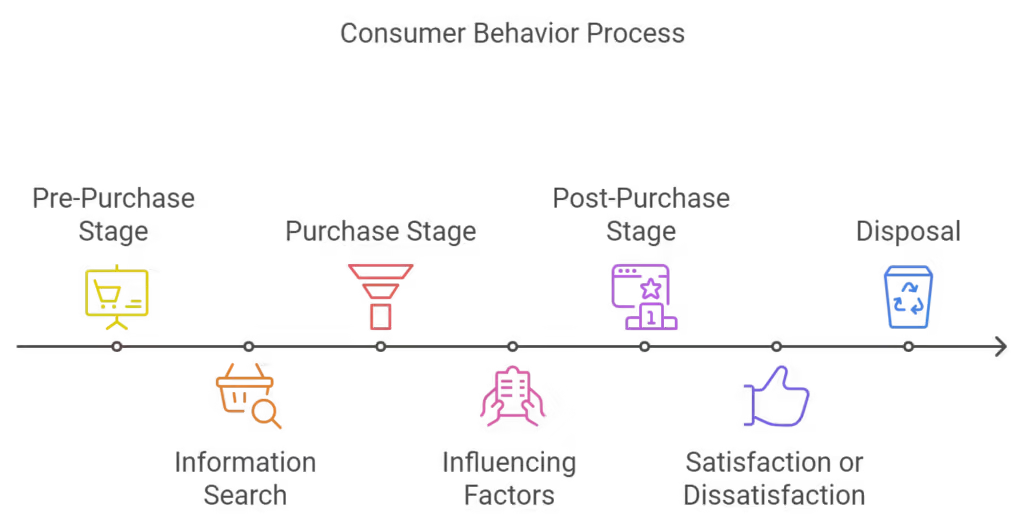
The consumer behavior process spans pre-purchase information gathering, purchasing decisions, and post-purchase evaluation.
Internal Factors Influencing Consumer Decisions
Psychological Factors: Motivation, Perception, and Learning
Psychological factors, such as motivation, perception, and learning, are at the core of consumer decision-making.
- Motivation: This drives consumers to fulfill their needs and desires. Motivations can be biogenic (e.g., hunger) or psychogenic (e.g., status). Understanding consumer motivation helps brands tailor their products to meet both functional and emotional needs.
- Perception: Perception is how consumers interpret marketing messages and product information. Each consumer’s perception is subjective, shaped by personal experiences and beliefs. For example, a well-designed package can create the perception of high quality, while poor branding may drive consumers away.
- Learning: Consumers’ purchasing behavior is often shaped by past experiences. Positive experiences build trust, which can lead to repeat purchases, while negative experiences lead to brand avoidance.
Personal Factors: Age, Life Cycle, and Personality
Personal factors like age, life stage, and personality also influence consumer behavior. As consumers progress through different life stages, their needs and preferences change.
- Age and Life Cycle: Young consumers might prioritize fashion and tech, while older consumers may focus on health products or retirement services. Brands that recognize these shifts in priorities can cater to evolving needs effectively.
- Personality: Consumers often choose products that reflect their personalities. For example, an adventurous consumer might gravitate toward travel gear or outdoor brands, while a luxury-loving individual might prefer high-end products that enhance their status.
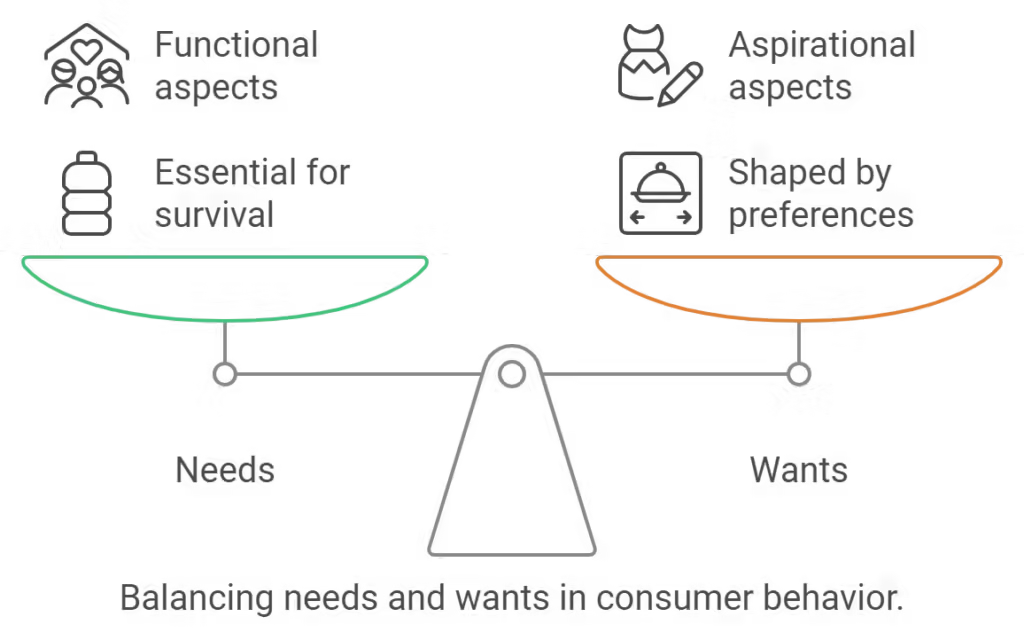
The balance between essential needs and personal wants plays a significant role in shaping consumer behavior.
Motivation: What Drives Consumer Actions?
Biogenic vs. Psychogenic Needs
Consumers are motivated by both biogenic needs, such as food, water, and shelter, and psychogenic needs, which include emotional and psychological desires like belonging and esteem. While biogenic needs are essential for survival, psychogenic needs play a critical role in shaping consumer preferences and brand choices.
For example, while everyone needs food, some may be motivated to choose organic or gourmet products because of psychogenic needs like social status or self-actualization.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and Buying Behavior
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a useful framework for understanding consumer motivation. This hierarchy progresses from basic physiological needs (food, water) to more complex psychological needs (esteem, self-actualization). As consumers satisfy lower-order needs, they move up the hierarchy and seek products that satisfy higher-order desires.
For marketers, positioning products according to where they fit on this hierarchy is critical. For instance, basic needs can be met by essentials like groceries, while self-actualization is often tied to luxury products or experiences that reflect personal achievement.
Perception and Learning in Consumer Choices
How Consumers Interpret Marketing Messages
Perception is critical in shaping consumer behavior, as it governs how individuals interpret and respond to marketing messages. Consumers may respond differently to the same marketing material based on their existing perceptions and beliefs.
For instance, two people may view the same ad for a fitness product—one may perceive it as motivating, while another may find it intimidating. Effective marketing needs to appeal to the target audience’s specific perceptions.
The Role of Past Experiences in Decision-Making
Past experiences play a significant role in shaping consumer preferences. If a consumer had a positive experience with a brand, they are more likely to buy from it again. Negative experiences, on the other hand, may lead them to avoid the brand altogether. Thus, building a strong, consistent customer experience is essential for long-term success.
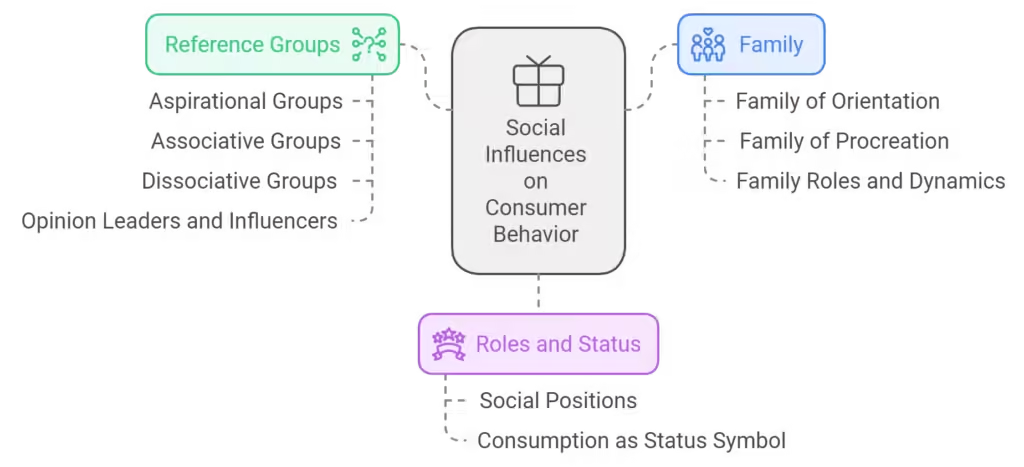
Social influences such as family, reference groups, and societal roles shape consumer behavior and purchasing decisions.
External Factors Shaping Consumer Behavior
The Influence of Social and Cultural Norms
Social and cultural norms significantly influence consumer behavior. These norms act as frameworks within which individuals make decisions about what is acceptable or desirable to purchase.
- Social Norms: Consumers often conform to the expectations of their social group. For example, luxury items like designer handbags may be purchased to fit in with peers in high-income circles. Social media amplifies these norms by showcasing what’s trendy or desirable.
- Cultural Influence: Culture dictates many purchasing decisions. Cultural norms influence what is acceptable, from dietary choices to clothing preferences. A brand’s success in different markets often depends on its ability to adapt to local cultural values.
Economic Factors: Income, Credit, and Purchasing Power
A consumer’s financial situation directly impacts their purchasing power. Economic factors like income, available credit, and economic trends influence how consumers approach spending.
- Income: Consumers with higher incomes have more discretionary spending power, often indulging in luxury or non-essential items. During economic downturns, however, consumers may prioritize essentials, seeking discounts and value-based options.
- Credit: The availability of credit can drive purchases of big-ticket items, such as cars or home appliances. Many companies offer financing options to make their products more accessible, boosting sales in the process.
Social Influence: The Power of Family, Peers, and Reference Groups
Family’s Role in Shaping Buying Habits
Family plays a significant role in consumer behavior, especially in shaping long-term habits. Early exposure to family consumption patterns—whether it’s the preference for a particular brand or shopping habits—can influence consumer choices later in life.
Peer Influence and Social Proof in Purchases
Consumers often rely on their social circle for purchasing cues. Recommendations from friends or influencers can sway opinions, as can the desire to fit in with a particular group. This is known as social proof, where consumers follow the behavior of others because it appears to be the right choice.
Cultural and Economic Influences on Buying Patterns
How Culture Shapes Consumer Desires and Actions
Cultural values heavily shape consumer behavior. In some cultures, collective decision-making is valued, meaning that group consensus influences purchases. In other cultures, individualism prevails, with personal preferences driving buying decisions. Marketers must adapt their strategies accordingly when entering new cultural markets.
Economic Trends and Their Impact on Purchasing Behavior
Economic conditions also play a key role in consumer behavior. During periods of economic growth, consumers may indulge in luxury items or non-essential goods. However, during economic recessions, consumers often pull back, focusing on saving and purchasing only essentials.
Emotional Triggers in Marketing
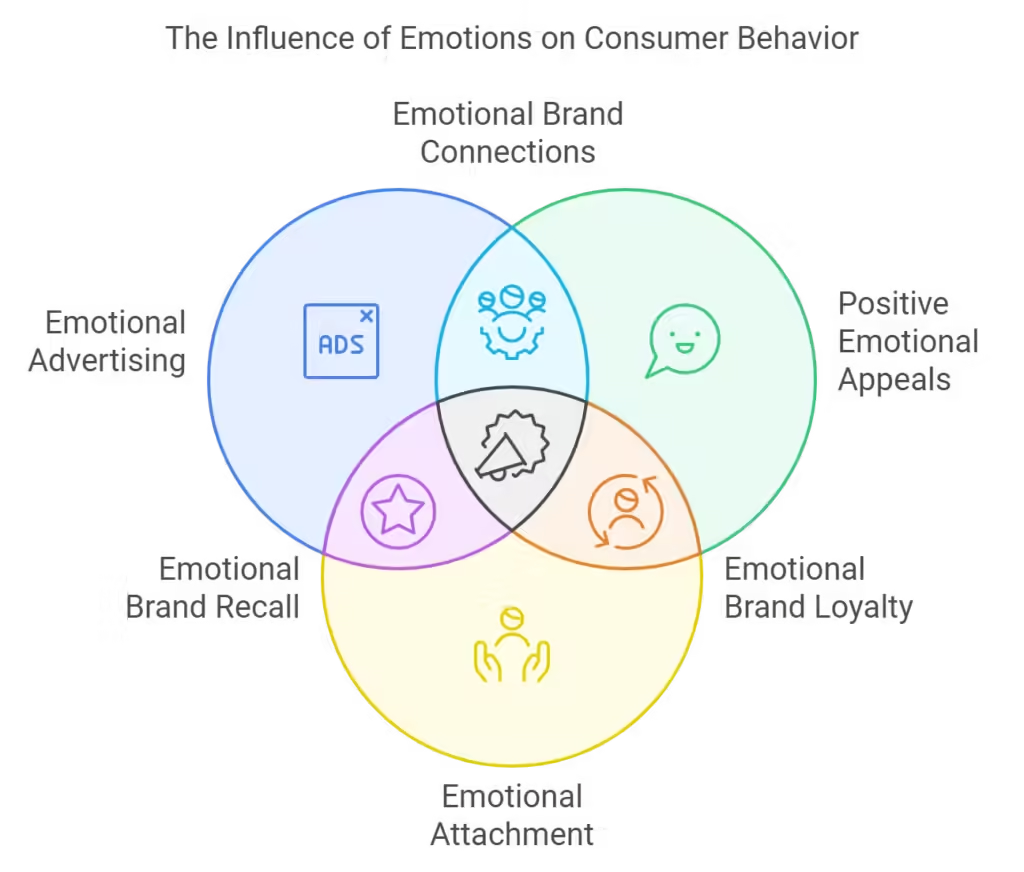
Emotional Advertising: Building Brand Connections
Emotions are powerful drivers of consumer behavior. Emotional advertising appeals to feelings like happiness, nostalgia, or even fear, creating a lasting connection between the brand and the consumer. Successful emotional campaigns go beyond the product itself, embedding the brand into the consumer’s life experiences.
How Emotional Attachment Overrides Rationality in Purchases
Emotional attachment often overrides logical thinking when making purchasing decisions. Consumers may continue to buy from a brand they are emotionally attached to, even when more affordable or practical alternatives exist. This emotional bond is crucial for fostering long-term loyalty.
Normative and Environmental Influences on Behavior
Social Norms: What Is Acceptable to Buy?
Social norms dictate what consumers perceive as acceptable or desirable. These unwritten rules influence purchasing decisions, especially for products that signal status or identity. For example, owning certain brands may symbolize success or belonging to a particular social group.
The Power of Environmental Cues in Retail Settings
Retail environments are carefully designed to influence purchasing decisions. Environmental cues such as lighting, music, and even the layout of a store can drive impulse purchases. These cues often work on a subconscious level, leading consumers to buy without fully realizing why.
Unconscious Consumer Behavior
The Role of Habit and Automaticity in Buying
Much of consumer behavior is habitual. Consumers often purchase the same products repeatedly, not because they are the best option, but because it’s easier and familiar. Automaticity in shopping can be influenced by convenience, store layout, and branding.
Subliminal Influences on Purchasing Decisions
Subliminal influences, such as subtle messaging or environmental stimuli, can impact consumer behavior without conscious awareness. While the effectiveness of subliminal marketing is debated, many brands use this technique to subtly guide consumer choices.
Heuristics and Biases in Decision-Making
Price-Quality Heuristic: Does More Expensive Mean Better?
Consumers often use mental shortcuts, or heuristics, to make decisions. The price-quality heuristic is one such shortcut, where consumers assume that a higher price equals better quality. Brands can use this to their advantage by positioning their products as premium.
Anchoring Effect and Loss Aversion in Shopping
Cognitive biases like the anchoring effect (relying too heavily on the first piece of information encountered) and loss aversion (preferring to avoid losses over gaining equivalent rewards) play significant roles in how consumers evaluate products and make purchasing decisions.
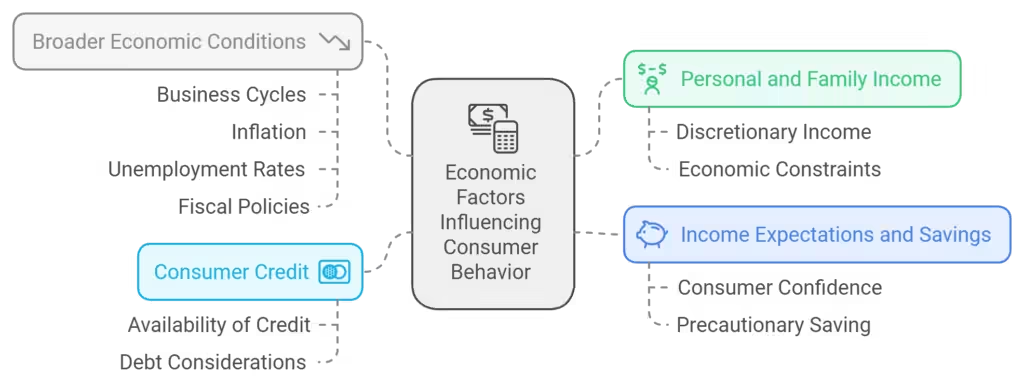
Economic factors like income, credit, and broader economic conditions affect consumer decisions and behavior.
The Impact of Technology on Consumer Behavior
E-Commerce and the Shift to Online Shopping
The rise of e-commerce has dramatically shifted consumer behavior. Online shopping offers convenience, variety, and often lower prices, leading many consumers to favor digital storefronts over traditional retail. The growing trend of mobile commerce (m-commerce) has further streamlined the shopping experience.
The Influence of Social Media and Digital Touchpoints
Social media platforms play a huge role in shaping consumer opinions. Influencers, peer recommendations, and targeted ads all contribute to a brand’s online presence, influencing the consumer’s journey from awareness to purchase.
Personalization and Big Data in Marketing
Using Algorithms to Predict Consumer Preferences
The use of big data and AI-driven algorithms allows brands to personalize their marketing efforts. By analyzing consumer behavior and preferences, companies can offer personalized recommendations, improving the consumer experience and driving sales.
Privacy Concerns and Ethical Considerations
While personalization enhances user experience, it raises concerns about privacy. Consumers are becoming more aware of how their data is used, pushing brands to be transparent and responsible in handling personal information.
Applications of Consumer Behavior in Marketing
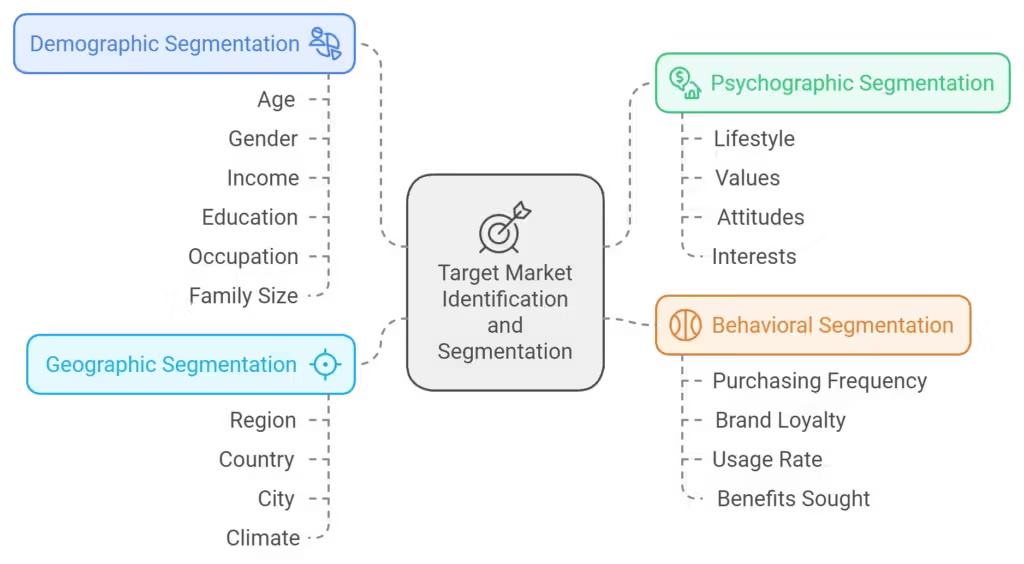
Developing Effective Target Market Strategies
Understanding consumer behavior allows marketers to segment their audience more effectively, targeting specific demographics with tailored products and marketing messages. By identifying niche markets and aligning products with consumer desires, brands can maximize their reach and relevance.
The Role of Product Positioning and Differentiation
Effective product positioning differentiates a brand from its competitors. By highlighting unique features, benefits, or emotional appeals, brands can occupy a distinctive space in the consumer’s mind.
Crafting Compelling Marketing Messages
Emotional vs. Rational Appeals
Marketers must strike the right balance between emotional and rational appeals in their messaging. Emotional appeals often build stronger connections with the audience, while rational appeals provide the logical reasons consumers need to justify their purchases.
Consistency Across Communication Channels
Consistency is key in marketing. Brands must ensure that their messaging is uniform across all channels—whether through social media, email, or traditional advertising. This builds trust and reinforces brand identity.
Ethical Considerations in Influencing Consumer Behavior
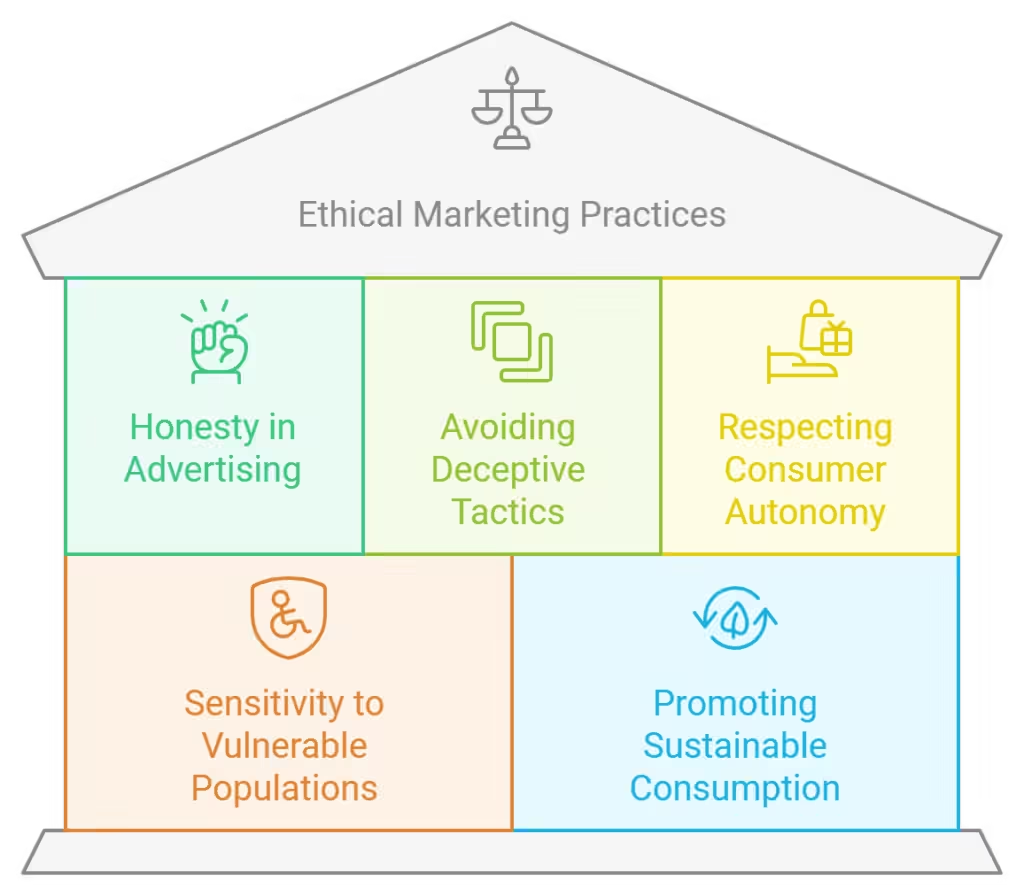
Responsible Marketing Practices
Ethical marketing practices are becoming more important as consumers demand transparency and fairness. Brands must avoid deceptive practices and ensure that their claims are truthful and verifiable.
Avoiding Exploitative Tactics and Promoting Sustainable Choices
Brands must avoid manipulative tactics, such as exploiting vulnerable populations. At the same time, promoting sustainability and ethical consumption has become a powerful differentiator in a market where consumers are more socially conscious than ever.
Conclusion: Understanding Consumer Behavior for Marketing Success
Adapting to the Ever-Changing Consumer Landscape
Consumer behavior is constantly evolving due to shifts in technology, culture, and economics. Successful marketers are those who remain agile, continuously learning and adapting to stay ahead of trends.
The Future of Consumer Behavior Research
As technology continues to advance, future research will likely focus on the impacts of AI, big data, and immersive technologies like AR/VR on consumer behavior. Understanding these trends will be key for brands looking to stay competitive in the future.



Leave a Reply